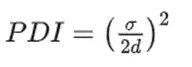Unlike other active molecules, antitumour drugs have cytotoxicity issues and therefore need to be safely encapsulated and able to reach their target sites, all of which is made possible by the use of nanoparticles. In addition, nanoparticles have unique features such as loading of insoluble antineoplastic drugs, protection of the active fraction from harsh in vivo environments, sustained release, alteration of their biodistribution, targeting to specific cells/tissues and prolonged circulation time.
The application of Quality by Design (QbD) methodology has driven the development of standardised procedures that are formulation-driven to obtain optimised products. The benefits of scaling up such nanoparticles could improve the therapeutic efficacy of not only traditional drugs, but also next-generation drugs.
About QbD
The Quality by Design (QbD) methodology is a systematic approach that emphasises the development of a product and process understanding and the development of a process control system for the manufacturing process based on predetermined quality objectives from the outset of the drug product development process. In the QbD approach, the establishment of a Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP) is the first step in the product development cycle to obtain the desired quality characteristics, including Critical Material Attributes (CMA), Critical Process Parameters (CPP), and Critical Quality Attributes (CQA).
Critical Process Parameters for High Pressure Homogeniser (HPH)
Homogenising Pressure
Homogenising pressure is the pressure that forces a liquid through a narrow gap, where the liquid droplets undergo shear, cavitation and turbulence to break up into smaller droplets. Droplets will only break up if they experience a sufficient amount of shear to overcome the Laplace pressure. An increase in pressure produces a higher pressure drop, which will easily overcome the Laplace pressure and lead to a decrease in size. The particle size of the drug changes depending on the drug concentration, solvent used, polymer type and number of cycles of the premix.
Number of cycles
A cycle is considered complete when the collected premix has been circulated through a narrow gap under specified pressure conditions. The droplet size is further reduced as the liquid again undergoes all the shearing, cavitation and turbulence.
For paclitaxel human serum albumin nanoparticles, after evaluating the effect of 6, 9, 12 and 15 cycles, 12 cycles were applied for further treatment. Twelve cycles were chosen because there was not much difference in the average diameter size with further increase in the number of cycles. Also the effect of the solvent used and the amount of drug added should not be ignored, they also have an effect on the particle size. Therefore, depending on the different material properties of the emulsion at constant pressure, increasing the number of cycles will reduce the droplet size to some extent.
Key quality properties of polymer nanoparticles
Average particle size / average droplet size
In general, there are two basic methods for defining particle size. The first method is to examine the particles and actually measure their size. For example, microscopy allows many size parameters to be measured from particle images. The second method uses the relationship between the behaviour of a particle and its size. This usually means using the size-dependent properties of the particles and relating them to the linear dimension to establish the assumption of an equivalent spherical size.
Due to enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects, particles smaller than 100 nm in size are able to cross the tumour's leaky vascular system and are more likely to passively target tumour cells.
Polydispersity Index (PDI)
The PDI is defined as the standard deviation (σ) of the particle size distribution divided by the mean particle size (d) as shown in equation (1).The smaller the PDI, the higher the monodispersity of the sample.The PDI is an estimate of the homogeneity of the sample.
Shape
The bulk properties of the particles (e.g., size and shape) affect the performance of the system. These surface properties can vary with the choice of nanoparticle preparation method and the key parameters involved in that method. Nanoparticles have been reported to be prepared in various shapes such as rods, discs, hollows, etc., affecting the in vitro and in vivo release of drugs from their systems. In addition to shape, shape-related parameters (e.g., aspect ratio or edge geometry) also affect biological interactions such as transport properties, cell-particle interactions, and thus release kinetics.
Surface charge
Cell membranes carry a slight negative charge and cellular uptake is driven by electrostatic attraction. The electrostatic attraction between the membrane and positively charged nanoparticles favours adhesion to the cell surface, leading to uptake. Surface loading induces reconstruction of lipid bilayers of larger nanoparticles (4-20 nm). The surface charge can be tailored to suit the delivery system by appropriate selection of polymer and surfactant combinations.
Droplet Stability
Various stabilisers are used in order to form stable emulsions and prevent agglomeration, flocculation and Ostwald ripening of particles. For polymer nanoparticles, non-ionic polymers, such as PVA and Pluronics, are commonly used stabilisers. They act to reduce the interfacial tension and thus stabilise the emulsion.The HLB value becomes the criterion for the selection of stabiliser.
Drug loading and encapsulation rate
Anti-tumour drugs should be loaded efficiently so that both loading capacity and encapsulation rate are successfully optimised.
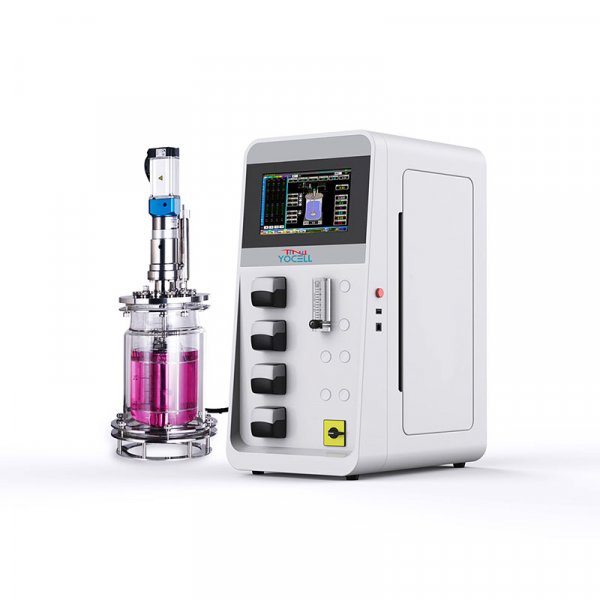
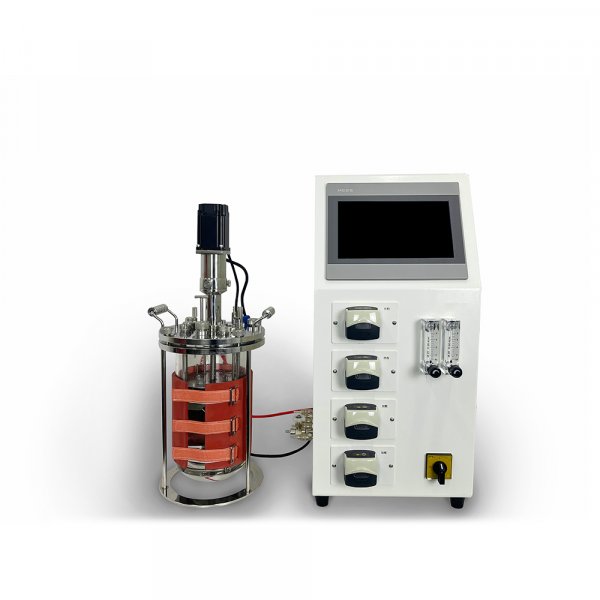
Yocell focusing on the R&D and production of high pressure homogeniser, we can effectively control the drug particle size, the material homogenisation is high and the operation is simple. The company has a full set of complex preparation nano equipment research centre, support customers to send samples, to solve the process pain points, to provide a full range of high-pressure homogenizer products, can support from the laboratory to the production of different scales of application!