Since the discovery of antisense nucleic acid and RNAi phenomenon, the mechanism advantages and broad targets of oligonucleotide drugs have attracted the attention of the pharmaceutical community, and by 2003, a number of companies dedicated to the development of RNAi drugs have been established, however, unmodified oligonucleotide drugs have not achieved the expected efficacy in clinical trials and caused immune-related toxicity. Big pharma companies exited RNAi around 2010. As chemistry addresses safety issues with technological developments suitable for delivery systems, the field of oligonucleotide drugs has entered the harvest period since 2016.
At present, 15 oligonucleotide drugs have been approved, and the current Gal-NAc technology is promoting the full entry of small monk drugs into the field of chronic diseases, which is expected to bring better compliance and effectiveness, from rare diseases to common diseases, and the commercial value of oligonucleotide drugs is expected to usher in a substantial increase.
Oligonucleotide drugs refer to oligonucleotide sequences with a general length of less than 30nt, mainly divided into ASO (antisense oligonucleotides), si RNA (small interference RNA), mi RNA (microRNA), Aptamer (aptamers), etc. At present, the common preparation method is phosphoramidite solid-phase synthesis.
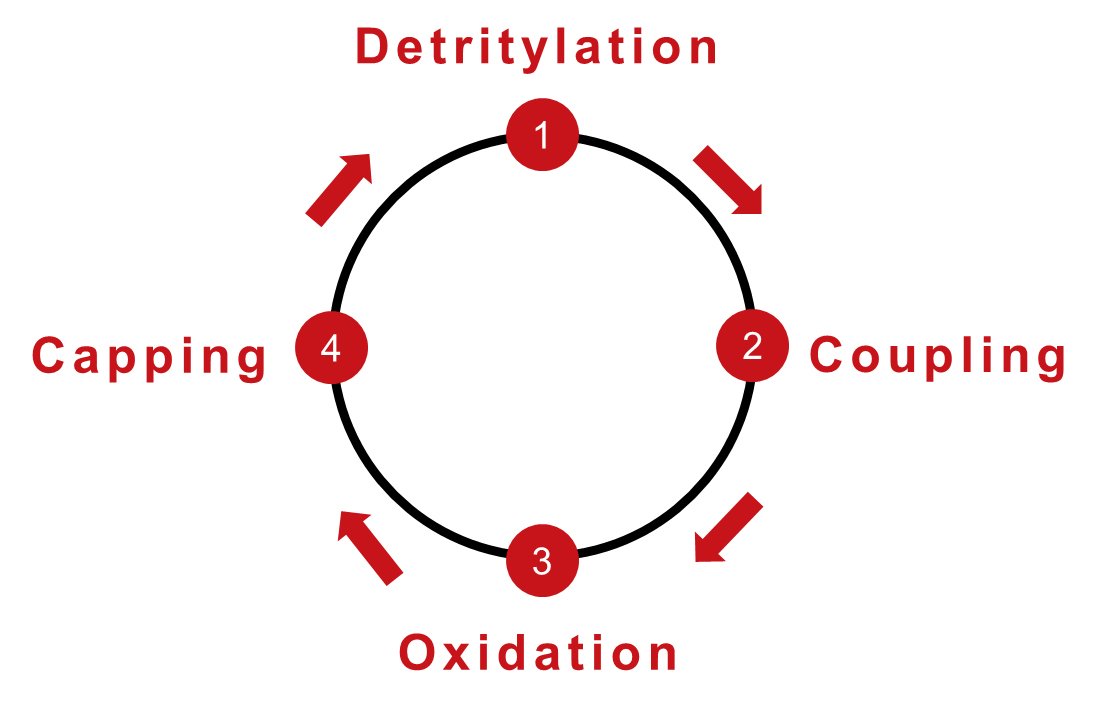
Phosphoramidite solid-phase synthesis is mainly divided into the following four steps:
1. Deprotection: remove the protection of the most terminal base, and then activate the protected amide online
2. Coupling: coupling the active amide by pumping the activated amide to the column bed
3. Oxidation (thiogeneration): oxidation to stabilize the phosphate skeleton structure
4. Cap: Seal any unprotected 5' ends
After these four processes, a sequence can be added to the fixed load, and the sequence can theoretically be added indefinitely from the 3' to 5' end by repeating this loop. Since the chemical reaction cannot be carried out completely, the coupling efficiency cannot reach 100%. However, the higher the coupling efficiency, the higher the yield of the target product and the lower the purification difficulty. The key to oligonucleotide synthesis is not only greatly affected by the quality of monomer, the quality of reagents, the process parameters of synthesis, and the humidity of the environment during synthesis, but also by the synthesis equipment used.




